Low ejection fraction of the heart treatment. The norm of the ejection fraction of the heart on ultrasound: how to determine the reasons for the decrease in the rate
To evaluate the work of a continuously running human "motor", many quantitative indicators are taken into account. Among them are cardiac output (EC) and cardiac ejection fraction (EF).
The norm of these values and comparison with them of the values measured in a particular patient allow the doctor to get an objective idea of the functional reserves of the “pumping” function of the myocardium and the pathologies present in his cardiovascular system.
The information, photos and videos in this article will help the average person understand the essence of these parameters, how they are measured, what affects the performance of VS and FVS, and whether modern medicine influence the body to normalize these values.
Cardiac output is the total volume of blood coming from the heart into the main vessels for a certain period of time or the volumetric blood flow velocity. Usually, the time unit is 1 minute, so among physicians the term "Circuit Minute Volume" or its abbreviation "IOC" is more often used.
Factors affecting the value of cardiac output

Cardiac output depends on:
- age and anthropometric indicators;
- human condition - rest (preload), after physical activity, psycho-emotional background;
- the frequency of myocardial contractions and its qualitative characteristics - stroke or systolic blood volume (SVS) from the left ventricle to the aorta, and from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery, during their contraction;
- the value of "venous return" - the blood volume flowing into the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cava, into which blood from the whole body is collected;
- thickness dimensions muscular wall and volumes of the heart chambers (see the figure above).
For your information. The VS parameter is also affected by specific indicators of the pumping (contractile) capacity of the cardiac apparatus and the current state of the general resistance to blood flow in the system of peripheral blood vessels of the general circulation.
Reference values and normative evaluation parameters

Today, it is quite easy to find out the exact indicators of cardiac hemodynamics. Most of them are calculated by a computer program during a non-invasive echocardiographic ultrasound examination.
The procedure can be done for free in a public clinic, performed in a private medical institution or laboratory, and even a specialist with a portable device can be called to your home. The price of the examination ranges from 700 to 6,500 rubles, and depends on the class of equipment.

There are other methods for determining VS and SVS - according to Fick, thermodilution, left ventriculography, Starr's formula. Their implementation is invasive, so they are used in cardiac surgery. The description of their essence will be clear only to specialists, but for the layman we will clarify that they are intended to control the state of cardio-vascular system during operations, monitoring the patient's condition in intensive care, but some are sometimes performed to make an accurate diagnosis.
Whatever methods of measuring VS are used, its reference values in a healthy adult who is in physical rest and psycho-emotional balance are fixed in the range from 4 to 6 l / min, while for one contraction from the left ventricle to the aorta is pushed out from 60 to 100 ml of blood. Such indicators are considered optimal, provided that the heart beat at a speed of 60-90 beats / min, the upper pressure was in the range from 105 to 155., and the lower - from 55 to 95 mm Hg. Art.
On a note. Unfortunately, EchoCG is not always enough to clarify the cardiological diagnosis. In addition to it, the doctor may prescribe CT tomography, PhonoKG, EFI, CT coronary angiography, radionuclide diagnostics.
Cardiac output syndromes
The decrease in VS occurs due to a decrease in the speed and volume of "venous outflow", as well as a violation of myocardial contractility.

Causes of low cardiac output syndrome include:
- Diseases or conditions caused by cardiac origin or complications after cardiac surgery:
- bradyarrhythmia, tachyarrhythmia;
- heart valve defects;
- end-stage congestive heart failure;
- metabolic disorders in the myocardium;
- occlusion of a shunt or a great vessel;
- decrease in blood volume;
- accumulation of air in pleural cavity and compression of the lobes of the lungs;
- accumulation of fluid between the sheets of the pericardium;
- oxygen starvation of the myocardium;
- a shift in the acid-base balance of the body towards an increase in acidity (decrease in pH);
- sepsis;
- cardiogenic shock.
- Non-cardiac processes:
- massive blood loss;
- extensive burn;
- decreased nerve stimulation of the heart;
- sudden expansion of the veins;
- obstruction of large veins;
- anemia;
- carbon dioxide poisoning.
On a note. Aging of the body, prolonged physical inactivity, starvation, diets that lead to a decrease in skeletal muscle volume cause a stable syndrome of low cardiac output.

High VS is an adequate response of the heart in response to physical or psycho-emotional stress. The heart of a marathon runner is able to work at the maximum limit - with an increase in venous return and cardiac output by 2.5 times, pumping up to 40 liters per minute.
If the BC indicator is elevated at rest, then this may be a consequence of:
- the initial stage of hypertrophy of the heart walls - the "athlete's heart";
- thyrotoxicosis;
- arteriovenous fistulas;
- chronic mitral and aortic insufficiency with overload of the left ventricle;
- low hemoglobin;
- beriberi disease (avitaminosis B1);
- Paget's pathology (deforming osteodystrophy).
For your information. An increase in the load on the cardiovascular system during pregnancy causes an increase in BC, which after childbirth returns to normal by itself.
What is the ejection fraction of the heart
Among the criteria characterizing cardiac hemodynamics, one can also find more “complex” parameters. Among them is the Heart Ejection Fraction (EFF), which is the percentage of stroke systolic volume of blood expelled from the left ventricle during heart contraction to the volume of blood accumulated in it by the end of the period of relaxation of the heart muscle (diastole).
This indicator is used to predict any cardiovascular pathology.

Reference values
The norm of the ejection fraction of the left ventricle at rest is 47-75%, and with psycho-emotional and physical stress, its value can reach 85%. In old age, the rate decreases slightly. In children, the reference values at rest are higher - 60-80%.
The FVS value is determined during radionuclide angiography using the Simpson or Teicholtz formulas. The survey form indicates which formula was applied, since discrepancies within 10% are possible.
Cardiologists pay attention to FVS in cases when it drops to 45% and below. Such values are clinical symptom violations of contractile insufficiency and a decrease in the efficiency of the heart muscle. Indicators below 35% indicate irreversible processes in the myocardium.
For your information. At the initial stage of any cardiac disease, the heart fraction ejection rate does not change due to adaptive processes - thickening of muscle tissue, restructuring of small-diameter vessels and alveoli, an increase in strength and / or number of contractions. A change in the value of the FVS occurs when the compensations are exhausted.
Reasons for the decline
Low cardiac output fraction occurs due to:
- diseases, infectious and inflammatory processes and myocardial defects;
- a large load on the heart due to pulmonary hypertension;
- pathology of the coronary and pulmonary vessels;
- tumor formations and diseases of the thyroid and pancreas, adrenal glands;
- diabetes, obesity;
- poisoning with alcohol, tobacco, drugs,.
Attention! Increasingly, there are cases of a decrease in the contractile work of the myocardium in young and mature people who abuse energy drinks.
Symptoms

Although a low cardiac output fraction in itself is a clinical symptom, it has its own characteristics manifestations:
- increased respiratory rate, possible attacks of suffocation;
- pre-fainting states and fainting;
- "flies" or "darkening" in the eyes;
- increase in heart rate to tachycardia values;
- puffiness lower extremities(feet, shins);
- numbness of hands and feet;
- a gradual increase in the size of the liver;
- pain syndrome (of different nature and strength) in the region of the heart and abdomen.
Important! Often, people suffering from diseases that are accompanied by a low ejection fraction of the heart look like drunk. Their coordination of movement is disturbed, their gait becomes unsteady, their tongue is tangled, and other speech defects occur.
How to increase the ejection fraction of the heart
Treatment of low ejection fraction of the heart is aimed at stabilizing pathological processes, and occurs as part of the standard therapy for a disease or condition that has caused a decrease in myocardial performance, and correction of left ventricular failure. In addition to hypertensive drugs, blood thinning antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, statins, peripheral vasodilators, antiarrhythmic drugs, aldosterone and angiotensin 2 receptor antagonists can be prescribed.

If the Cardiac Ejection Fraction falls below 35%, therapeutic measures are aimed at improving the quality of life. If necessary, resynchronization therapy (artificial blockade) is performed. In cases of fatal arrhythmias, a pacemaker or a cardiovector defibrillator is placed.
And at the end of the article, watch a video with detailed instructions for performing an exercise from Chinese health-improving gymnastics that is accessible to everyone, which will help improve the cardiovascular system at the energy level.
Such a value as the ejection fraction of the heart, is characterized by the amount of blood released into the aorta during contraction. If this indicator decreases, this indicates a deterioration in the performance of the organ and the possible occurrence of heart failure.
When the fraction is very low, less than 30%, then the person is in serious danger. At rest, the left ventricle stores the blood that has come from the atrium. With a contractile movement, it throws out a certain amount of it into the vascular bed.
The ejection fraction (EF) of the left ventricle is calculated as the ratio of the volume of blood entering the aorta to its amount in the left ventricle during relaxation. This is the percentage of the volume of ejected body fluid.
What it is
EF is considered a common indicator that an ultrasound machine can provide. These data indicate the quality of the work of the heart during contraction. During the entire process, the volume of blood that has left the left ventricle into the vascular bed is measured and displayed as a percentage.
.jpg)
Measurement is done in the left ventricle, from here blood is coming v big circle circulation. When the indicator drops, this indicates that the heart cannot contract at full strength and there is a lack of blood volume in the body. With minor violations, this situation can be corrected by medication..
Usually, studies are prescribed when a patient complains of shortness of breath, tachycardia, dizziness, fainting, fatigue, pain in the heart or behind the sternum, swelling of the extremities. Primarily shown biochemical analysis blood and electrocardiogram.
Sometimes Holter monitoring or ultrasound is performed for a complete picture.
How is the emission rate calculated?
There is a calculation formula. To do this, the stroke volume is multiplied by the heart rate. This is how you get the right size. The result will tell you how much volume is pushed out in one minute. In general, the normal indicator should reach approximately 5.5 liters.
Formulas for calculating the ejection fraction
In medicine, they also use special programs that automatically calculate the fraction. For this, the Teicholz formula, Simpson's method is used. At the same time, the data for these two calculations may differ by an average of 10%.
EF should be in the range of 50-60%, the Simpson norm suggests that the lower limit should not be less than 45%, and according to Teicholz 55%.

The Teicholtz formula uses systolic and diastolic volumes and the size of the left ventricle. The study involved a small part of the latter.
The overall length indicator does not matter.
Typically, the study is carried out on old equipment and in the presence of areas with impaired local contractility (for example, in the case of ischemia), the Teicholz formula may fail and a fuzzy result.
To get the EF, the amount of shortening is multiplied by a factor of 1.7. DU is obtained from the formula ((KDD - KSD) / KDD) * 100%. Where EDD is the end diastolic diameter, ESD is the end systolic diameter.
Simpson's formula is more modern, it accurately shows all significant areas of the myocardium, taking into account the geometry of the ventricle and the presence of areas with impaired local contractility through the apical 4- and 2-chamber section.

The Simpson method involves dividing the cavity of the left ventricle into thin discs and determining their boundaries. Outlined systole and diastole are visible along the contour of the cardinal surface of the ventricle; these data can be used to estimate the volume of ejection.
Norms for adults
The indicators do not depend on the patient's gender, therefore, the norms for women and men are identical. However, they may vary by age. The older the person, the lower his rate.
An EF of less than 45% is considered reduced. With indicators in the region of 40%, heart failure can be suspected.
If in adults the level is less than 35%, then this indicates that violations are occurring and the person is in danger. With hypertension, the indicator may increase, while in some people it may be extremely low, which is due to a physiological predisposition, but not less than 45%.
The norm in children
At a younger age, the figure may be higher. So, the norm in children from birth to 14 years is in the range of 60-80%. Nevertheless, it is impossible to consider only one EF, when making a diagnosis, all indicators of the work of the heart are taken into account.
The table of norms involves comparing height, weight, fraction and heart rate.
What studies are used to determine the indicator
If the doctor has a suspicion of a violation of the heart, he directs the patient to do a cardiogram and a biochemical blood test. Holter monitoring, electrocardiogram, bicycle ergometry and ultrasonography organ.
Doctors study all indicators at once and judge the presence of pathology by their total value. The main ones are the following:
.jpg)
- Cardiac output should be between 55 and 60%.
- The size of the right chamber atrium is 2.7-4.6 cm.
- The diameter of the aorta is 2.1-4.2 cm.
- The size of the left-sided atrium is 1.8-4 cm.
- The rate of stroke volume is 60-100 cm.
What does low mean
When the indicator is in the range of 55-75%, this is the norm. A reduced value is from 45 to 55%. When it is up to 45, it means that the patient has heart failure. If it is below 35%, then irreversible disturbances in the work of the organ occur and the person needs urgent treatment.
.jpg)
Reasons for downgrading
The indicator can be reduced with the following pathologies:

- Myocardial infarction. When scars appear on the muscles and they cannot contract properly. Moreover, after a heart attack, it is not possible to increase the fraction by medication.
- coronary disease. This reduces blood flow.
- Failure of the rhythm of contractions. It leads to impaired conduction, wear and tear of the heart.
- Cardiomyopathy. Causes an increase in muscle size.
Identification of pathology in the early stages and its elimination through drug therapy can save the situation. If nothing has been done, then gradually the EF decreases even more.
This is due to the fact that the heart muscle begins to change, its layer grows, the structure of small blood vessels deteriorates, fibers weaken and blood absorption decreases.
In addition, the causes of pathology can be hidden in:
.jpg)
- Angina.
- Hypertension.
- Pericarditis, endocarditis, myocarditis.
- Aneurysm of the walls of the ventricle.
- Congenital malformations of an organ or blood vessels.
- Vasculitis.
There are predisposing factors that can also disrupt the functioning of the organ. These include obesity, tumors, severe intoxication, hormonal failure and diabetes.
Symptoms of a low rate
The main symptom, when the fraction is reduced, is the appearance of shortness of breath, and regardless of the load. It can appear even due to minor loads when doing homework. Sometimes shortness of breath can be at night or when lying down.
Among other signs, patients note:
.jpg)
- Increased weakness, fatigue and dizziness, up to loss of consciousness. This is due to a lack of blood supply and, as a result, oxygen starvation.
- The appearance of edema. This is due to stagnant fluid.
- Severe pain in the right side of the abdomen. This is noted due to congestion in the vessels of the liver, which can provoke further cirrhosis.
- Violation of vision.
- Pain in the area of the heart with an increase in the rhythm of contractions.
- Decreased sensation in the limbs.
- Impaired coordination.
- Nausea, vomiting.
How to increase the indicator value
First, the patient is diagnosed in order to identify the pathology that caused the decrease. Further, the administration of drugs corresponding to the diagnosis is prescribed. With ischemia, the use of nitroglycerin is indicated, with hypertension, antihypertensive drugs and surgical correction of defects are prescribed.
.jpg)
In addition to treating the underlying disease, the contractile function is stabilized. These include Digoxin, Korglikon, Strofantin.
So that the cardiovascular system is not overloaded with fluid, it is recommended to follow a diet, reduce salt and the amount of daily fluid.
Along with this, diuretics are shown that contribute to the removal of excess fluid: Veroshpiron, Diakarb, Diuver, Indapamide, Torasemide.
ATP inhibitors help strengthen blood vessels and thus protect the heart. When they are taken, tissue nutrition improves, the performance of the heart muscle and the resistance of the myocardium to stress increase. This group includes: Enalapril, Perindopril, Captopril.
They help reduce the organ's need for oxygen and nutrients, increase the volume of myocardial contraction sites, reduce cell death and heart rate. Their list includes: Nebivolol, Metoprolol, Bisoprolol.
Aldosterone receptor antagonists stabilize the electrolyte level of the blood, remove excess fluid, and reduce the load on the myocardium.

Representatives of the group are Spironolactone, Eplerenone. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists have a similar effect, but they are somewhat stronger. Assign Valsartan, Kandesartan, Olmesartan.
When ejection fraction is low, statins may be used as adjunctive therapy to lower cholesterol and protect blood vessels. Apply Pravastatin, Fluvastatin, Simvastatin.
Effective and anticoagulants that thin the blood and prevent atherosclerotic changes. This is Warfarin, Xarelto.
Other treatments
In addition to taking appropriate drugs, all patients need to reconsider their lifestyle in order to increase the fraction.
.jpg)
- Organize proper nutrition.
- Rest enough time.
- Undergo physiotherapy and reflexology.
- Control physical activity.
- Be outdoors often.
- Refuse bad habits.
Surgery
In case when drug therapy ineffective, surgical treatment may be prescribed.
Its common methods are:
- Installation of a cardioverter-defibrillator, a pacemaker in case of heart rhythm disturbance.
- Creating an artificial blockade to slow down the contraction of the ventricles in order to stimulate different rhythms of atrial and ventricular contractions.
home remedies
It is almost impossible to raise a faction by folk means.
Basically, this therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms and maintaining the health of the organs. So, to prevent swelling, take decoctions of calendula, milk thistle, horsetail, yarrow, knotweed, nettle, chicory, birch buds, juniper berries, rose hips, lingonberries. They need to be drunk in the intervals when medicines of a similar effect are canceled.

- A decoction of mistletoe, hawthorn and cudweed, taken in equal amounts, is considered effective. Two tablespoons of the mixture are poured with a liter of boiling water and put on a small fire. After a couple of minutes, the brew is set aside and insisted for about half an hour. Strain, take 125 ml three times a day.
- Dried hawthorn fruits in the amount of 6 tablespoons are rubbed and motherwort herb is added in the same amount. Bay mixture of 1.5 liters of boiling water, insist day, well wrapped. Then strain and place in the refrigerator. It is necessary to drink three times a day half an hour before meals, one glass each.
- In the treatment of cardiac pathologies, hawthorn is often used. It helps to normalize the heart rhythm, reduce hypertension, chest pain, fights atherosclerosis and heart failure. Hawthorn flowers and berries help the heart by increasing its ability to pump blood. This herb helps reduce shortness of breath and fatigue. Hawthorn can be used both as a tincture and as a decoction.
Willow bark, meadow clover, sweet clover, meadowsweet, hawthorn, and rakita are used to thin the blood.
Relief fees include:
- Composition of hawthorn, cudweed, chamomile, cumin and motherwort.
- A decoction of St. John's wort, mistletoe, sage, yarrow, cudweed, calendula, horsetail and pine buds.
For these purposes, you can purchase ready-made tinctures of peony, valerian, motherwort or hawthorn at the pharmacy. In the absence of herbs, 50 g of honey can be diluted in 500 ml of water and drunk in 4 doses during the day.
When a high fraction value is diagnosed
An increase in the indicator is rare, since it is physiologically impossible. The heart cannot expel more blood than it should. Therefore, the level of 80% can occur in a child at an early age, athletes and patients leading an active lifestyle.
Sometimes an increase indicates myocardial hypertrophy, when the left ventricle seeks to compensate for the onset of CHF and pushes blood out with considerable force.

If the indicators do not correspond to the norm, it is imperative to consult a cardiologist and undergo an echocardioscopy to prevent the development of pathologies.
Consequences
If you do not pay attention to the problem, then severe chronic heart failure develops. Moreover, the body experiences a lack of oxygen, since the blood is pushed out in insufficient quantities and does not carry all the necessary nutrients.

Oxygen starvation can lead to serious pathologies of both the heart and the brain.
Health prognosis
The prognosis depends on how low rate diagnosed in a patient. When the value is lowered to 40-45%, the risk of cardiac arrest is small, about 10-15%. When the EF decreases to 34-39%, then the possibility lethal outcome is in the range of 20-25%.
If this indicator becomes even lower, then the threat to life for the patient increases as the EF decreases.
It is not possible to completely get rid of the pathology, therefore, patients with this diagnosis must constantly undergo corrective therapy, which will allow them to maintain their vital functions for many years.
The ejection fraction provides information about the performance of the left ventricle. In men and women, the norm is the same (55-70%), but in children the figure can reach 70-80%, which is not considered a pathology.
The most common is the low fraction. To raise the rate, it is necessary to find the cause of the pathology and organize adequate treatment. If this is not done, the patient is threatened with the development of heart failure, death.
Ejection fraction of the heart (EF) is an indicator by which the quantitative volume of blood ejected into the aorta during the conduction of an electrical impulse in the left ventricle is fixed.
Ejection fraction of the heartPayment this indicator occurs by the ratio of blood that enters the largest vessel, to the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle when its tissues are weakened.
This value, simply calculated, stores a lot of information regarding the possibility of contractions of the heart muscle. The definition of EF affects the prescribed medicines for the heart, and the prediction of life for people with heart failure is also made according to EF.
The closer the EF values to the norm, the better the heartbeat occurs. If the ejection fraction deviates below normal, this indicates that the heart is not able to contract at a normal rate, which leads to impaired blood circulation.
In such a situation, you need to urgently consult a doctor for qualified help.
How is PV calculated?
The calculation of this fraction is not difficult, but it contains a fairly large amount of information about the heart muscle and its ability to normal contractions.
In many cases, Doppler ultrasound of the heart is used to determine the ejection fraction.
 PV calculation.
PV calculation. The fraction index is calculated using the Teicholtz formula, or by the Simpson formula. All calculations are made with the help of a program that automatically gives the result, depending on the amount of blood in the unstressed left ventricle, pushed into the aorta.
The main differences between the above formulas are:
- According to the Teicholtz formula, the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle is determined using the M-modal ultrasound examination. This formula was patented by Teicholtz in 1976.
- A small part of the ventricle at its base is examined, the length is not taken into account. False results obtained by the formula may occur when ischemic attacks when contractions are impaired in certain areas of the heart muscle.
- The program takes into account information about the volume in the relaxed and contracted left ventricle, giving the result automatically. This method is used on equipment that is this moment obsolete;
- According to the Simpson formula, a quantitative two-dimensional ultrasound examination of the heart is performed, with the help of which more accurate results are obtained. Simpson's algorithm was patented by him in 1989. Identical name this algorithm is the disk method. In this study of ejection fraction, all important areas of the heart muscle are examined.
Fact! Indicators of the results of the study of the same patient, according to different formulas, can fluctuate with a difference of ten percent.
What are the features of the FW?
The main features inherent in the ejection fraction are the following:

Norms
Individual indicators of the ejection fraction are considered normal for a person, since for different age categories of people, its levels can vary. Also, the levels of the ejection fraction norm depend on the calculation formula and the equipment on which the analysis is carried out.
Average generally accepted normal value:
- For Simpson's formula is fifty to sixty percent, with the lowest bar being forty-five percent;
- According to the Teicholtz formula, the lowest bar is fifty-five percent. The indicator of the lower bar determines what exactly such a percentage of blood needs to be squeezed into the aorta in order for the right amount of oxygen to reach the organs.
- In case of heart failure, the indicators range from thirty-five to forty percent. In this condition, medical maintenance of the body, or surgical intervention is necessary.
- At rates below 35 percent, early burdens can occur, as well as death.
 V childhood ejection fraction indicators are slightly increased. In newborns, it is no less than sixty percent and can reach eighty. As the body develops and the child grows, the level of ejection fraction returns to normal.
V childhood ejection fraction indicators are slightly increased. In newborns, it is no less than sixty percent and can reach eighty. As the body develops and the child grows, the level of ejection fraction returns to normal.
With deviations, in most cases, there is a decline in the ejection fraction, rather than its growth. Various pathological conditions affect the decrease in EF levels.
When the ejection fraction is below normal, this indicates that the myocardium cannot contract at a normal pace. It leads to impaired blood circulation in the body and oxygen starvation of organs. Initially, the brain suffers from hypoxia.
In some cases, the results of the study show the boundaries of the ejection fraction above 60 percent. In many cases, they do not exceed 80 percent, since a healthy left ventricle cannot eject more blood into the aorta due to its structural features.
 The structure of the heart.
The structure of the heart. Also, with a pathological increase in the heart muscle, an increased ejection fraction may indicate that the myocardium cannot recover from progressive heart failure and is trying to eject the largest amount of blood into the aorta.
As heart failure progresses, ejection fraction decreases. That is why it is important to monitor the deviations of EF in one direction or another, and immediately go to the hospital for examination.
Why is there a decline?
The starting stages of the progression of heart disease do not affect the ejection fraction. This happens because the heart muscle is trying to adapt to changes (the layer of the myocardium increases, its contractions become more frequent, and the small vessels of the heart are rebuilt). Familiarize yourself with what a heart muscle is.
With the development of the disease, the muscle wears out more and more, which leads to deviations in functional abilities that lead to structural disorders. All this disrupts the amount of blood ejected from the left ventricle into the aorta, causing disruptions in blood circulation.
Such deviations provoke everything that negatively affects the heart muscle:
| Factor | Characteristic diseases |
|---|---|
| Decline in normal blood flow through the coronary arteries | Various forms of angina pectoris; |
| Death of the heart muscles; | |
| Scar formation on the walls of the myocardium; | |
| A form of ischemic attack that occurs without symptoms; | |
| Expansion of the walls of the stomach; | |
| Constant increase in pressure. | |
| Diseases of infectious and inflammatory origin | Myocarditis (the muscular membrane is affected); |
| Endocarditis (changes on the inner shell); | |
| Pericarditis (disease of the heart bag). | |
| Structural changes in the tissues of the heart muscle | All types of primary myocardial lesions not associated with inflammatory, tumor and ischemic excitations; |
| Deviation of metabolism in the myocardium, which leads to the thinness of the heart walls. | |
| Deviations in the structure of the structure of the heart, formed in the womb; | |
| Violations of the structure of the heart due to damage by rheumatic diseases; | |
| Increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation. | |
| Pathological conditions of blood vessels | Inflammatory processes on the walls of blood vessels, which lead to their deformation; |
| Congenital abnormalities in the structure of the heart (improper arrangement of blood vessels, large narrowing of the aorta, improper connection of large vessels); | |
| Expansion of the aorta, provoked by the deformation of the walls of blood vessels; | |
| detachment of the aorta; | |
| Deposition on the walls of atherosclerotic plaques; | |
| narrowing of the aorta; | |
| Thrombosed pulmonary vessels. | |
| Failure in the endocrine system | Failure of the production of thyroid hormones; |
| Failure of glucose absorption in the body; | |
| The presence of diabetes; | |
| Tumor formations in the adrenal glands or pancreas; | |
| Excessive excess weight. | |
| Influence of toxic agents | Alcohol; |
| Drinks containing a high concentration of caffeine (strong tea, coffee, energy drinks, etc.); | |
| Cigarettes; | |
| The use of narcotic drugs; | |
| Taking certain medications (cardiac glycosides). |
Deviation symptoms
Violation of physical and labor activity are the main consequences of violation of the normal boundaries of the ejection fraction of the heart. There is a significant deterioration in the state in which daily activities become difficult to perform.
In most cases, with circulatory disorders, the following symptoms appear:

If one of the above symptoms is detected, it is urgent to go to the hospital for examination.
How are low scores treated?
Since a decrease in ejection fraction is not a separate disease, but only provoked by the initial diseases, a qualified doctor should send the patient for additional hardware examinations that will help determine the root cause of the decrease in EF.
Depending on the cause that provoked a decrease in ejection fraction, treatment can be:
- medication;
- Surgical.
With ischemic attacks, it is necessary to take nitroglycerin to normalize EF, and for hypertension, antihypertensive drugs, etc.
It is important to understand that with a decrease in EF, heart failure progresses, which requires compliance with all doctor's recommendations.
Preparations
The main drugs that affect the increase in ejection fraction are listed in the table below.
| Medicine groups | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| ACE inhibitors (enalapril, ramipril, captopril) | Expand blood vessels; |
| Improve nutrition of myocardial tissues; | |
| Increase the resistance of the heart muscle to stress; | |
| Increase myocardial performance | |
| Beta-blockers (Nebivolol, Bisoprolol, Metoprolol) | Reduce the needs of cardiac tissues for saturation with oxygen and useful elements; |
| Reduce the frequency of heart contractions; | |
| Reduce the rapid wear of the heart muscle; | |
| Increase the number of zones that contract the heart muscle. | |
| Aldosterone receptor antagonists (Eplerenone, Spironolactone) | Recovery normal level potassium and sodium in the blood; |
| Removal of fluids from the body, which reduces the load on the heart muscle. | |
| Diuretics (Torasemide, Indapamide, Hypothiazid) | Remove accumulations of fluid; |
| Reduce the effect on the heart muscle. | |
| cardiac glycosides (Digoxin, Strofantin) | Improvement of myocardial contractions; |
| With impaired functionality of the heart muscle, the conduction of electrical impulses is restored. | |
| Angiotensin II receptor antagonists (Olmesartan, Valsartan, Candesartan) | They have the same effect as ACE inhibitors, but the acting force is much greater. |
Additional tools that can improve the ejection fraction in individual cases include the following.
There are also groups of drugs that are auxiliary and are prescribed, in
individual situations, in combination with the main therapy.
| Drug groups | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Peripheral vasodilators (Nitroglycerin, Sodium, Nitroprusside, Apressin) | Significantly reduce the load on the ventricles; |
| Helps improve blood circulation in the vessels of the heart. | |
| Calcium channel blockers (Nifedipine, Verapamil, Nimodipine) | They contribute to an increase in the lumen of the vessels of the heart, which leads to a greater consumption of nutrients by tissues. |
| Disaggregants (Plavix, Aspirin) | Prevent the formation of blood clots. |
| Means against arrhythmia (Amiodarone, Diltiazem, Disopyramide) | Restore heart rhythm when it is disturbed. |
Surgical intervention
When the ejection fraction is deviated, surgical interventions can be used. The type of surgical operation depends on the individual parameters and pathological conditions of the patient.
In most cases, the following operational methods are used:
- Implantation of a defibrillator or pacemaker. Through open heart surgery, a device is installed that, in case of heart rhythm disturbances, restores normal blood circulation by electrically acting on the heart;
 Heart stimulator.
Heart stimulator. - Impact on different rhythms of the ventricles and atria. Achieve a slowdown in ventricular contractions, with the help of artificial heart block. This restores the necessary flows of blood entering the ventricles.
What will help improve the condition, in addition to the main course of treatment?
For complex treatment the following recommendations must be followed. Only by observing them, and correctly prescribed method of treatment.
Long-term ejection fraction normalization can be achieved:
- Normalize the daily routine, allocating time for a good sleep (at least 8 hours);
- Moderate physical exercise. Necessary for the speedy recovery of the myocardium damaged by the underlying causes. It is important not to overdo it so as not to damage the heart muscle;
- It is recommended to go in for non-heavy sports (physical education, swimming, aerobics, etc.), as well as allocate at least one hour a day for walking;
- Avoid strong physical exertion;
- Healthy food. And also consume more food rich in iron;
- Massage is recommended to improve blood circulation and relieve swelling;
- Avoid stressful situations. Strong emotional stress (both positive and negative), constant stress, depression - all this affects the deformation of the myocardium, due to its overstrain;
- Maintain normal water balance. Drink at least one and a half liters of clean drinking water per day;
- Reduce salt intake;
- Get rid of bad habits. Toxins supplied with alcohol and cigarettes irritate the myocardium.
You can take blood thinners:
- Willow bark - prevents the formation of clots, thinning the blood;
- Meadow clover. Concentrates salicylic and coumaric acids. Regular intake of such a decoction reduces the density of the blood;
- meadowsweet. Contains the same acids as clover, plus ascorbic acid. It has a positive effect on the body, strengthening blood vessels, fighting rheumatism, and killing bacteria;
- Sweet clover is yellow. Contains a high concentration of coumarins, which slow down clotting;
- Hawthorn is a fairly common plant. Its leaves strengthen blood vessels, have a positive effect on the heart, and also thin the blood. For medical purposes, it is used as alcohol tincture or extract;
- Rakita. Bushy plant, with a high concentration of flavonoids and salicylates. Prevents inflammation and tones, inhibits coagulation processes and strengthens blood vessels. For the purpose of treatment, the bark is used;
- Ginko Biloba. The most powerful antioxidant, dilates blood vessels, preventing blood clots from forming. It has a positive effect on blood flow in the brain, improving memory and attention.
Also, sometimes they use means to calm the body, since under the emotional and nervous influence, the aggravation of heart diseases is aggravated.
These include:

There are also the following methods to calm the nervous system:
- Garlic with milk. For cooking, you need to grate a clove of garlic into milk, and consume half an hour before breakfast;
- Honey with water. Dissolve 50 grams of honey in half a liter of water, and drink in 4 doses throughout the day.
Attention! The use of any means traditional medicine requires prior consultation with the attending physician. Self-administration can lead to complications.
Prevention
In order to maintain a healthy state of the body, the following recommendations should be followed:
- If available excess weight, it is recommended to reset it;
- Avoid stressful situations and nervous tension;
- Adhere to the regime of the day, proper rest and sleep;
- Monitor blood pressure;
- Eat less animal fats, and more vegetable;
- Eat in a balanced way;
- Get rid of a sedentary lifestyle, play sports;
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
 Right way of life.
Right way of life.
What is the forecast for EF deviations?
If the ejection fraction falls to forty percent, then the risk of death from sudden cardiac arrest is up to fifteen percent. With a decrease to 35 percent, the risk is up to 25 percent. If the indicators fall below these levels, then the risk increases proportionally.
It is not possible to completely cure ejection fraction deviations, but early therapy will help prolong life with a normal life process.
In case of detection of any symptoms, or already diagnosed diseases, it is necessary to constantly monitor the cardiologist and regularly take tests. This is done to prevent the progression of complications.
DO NOT self-medicate and be healthy!
An important diagnostic method
Echocardiographic examination of the cardiovascular system is a very important and, moreover, quite affordable diagnostic method. In some cases, the method is the "gold standard", allowing you to verify a particular diagnosis. In addition, the method allows you to identify latent heart failure, which does not manifest itself during intense physical exertion. Echocardiography data ( normal) may vary slightly depending on the source. We present the guidelines proposed by the American Association of Echocardiography and the European Association for Cardiovascular Imaging from 2015.
2 Ejection fraction

The ejection fraction (EF) has an important diagnostic value, so allows you to evaluate the systolic function of the left ventricle and right ventricle. The ejection fraction is the percentage of blood volume that is expelled into the vessels from the right and left ventricles during the systole phase. If, for example, out of 100 ml of blood, 65 ml of blood entered the vessels, this would be 65% as a percentage.
Left ventricle. The norm of the left ventricular ejection fraction in men is ≥ 52%, for women it is ≥ 54%. In addition to the LV ejection fraction, the LV shortening fraction is also determined, which reflects the state of its pumping ( contractile function). The norm for the shortening fraction (FU) of the left ventricle is ≥ 25%.
A low left ventricular ejection fraction can occur with rheumatic heart disease, dilated cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, myocardial infarction, and other conditions that lead to the development of heart failure (weakness of the heart muscle). A decrease in left ventricular FU is a sign of LV heart failure. Left ventricular FU decreases in heart diseases that lead to heart failure - myocardial infarction, heart defects, myocarditis, etc.
Right ventricle. The norm of the ejection fraction for the right ventricle (RV) is ≥ 45%.
3 Dimensions of the chambers of the heart

The size of the chambers of the heart is a parameter that is determined in order to exclude or confirm atrial or ventricular overload.
Left atrium. The norm of the diameter of the left atrium (LA) in mm for men is ≤ 40, for women ≤ 38. An increase in the diameter of the left atrium may indicate heart failure in the patient. In addition to the diameter of the LP, its volume is also measured. The norm of LA volume for men in mm3 is ≤ 58, for women ≤ 52. The size of the LA increases with cardiomyopathies, defects mitral valve, arrhythmias (heart rhythm disturbances), congenital heart defects.
Right atrium. For the right atrium (RA), as well as for the left atrium, the dimensions (diameter and volume) are determined by the EchoCG method. Normally, the diameter of the PP is ≤ 44 mm. The volume of the right atrium is divided by the body surface area (BSA). For men, the ratio of the volume of PP / PPT ≤ 39 ml / m2 is considered normal, for women - ≤33 ml / m2. The size of the right atrium can increase with insufficiency of the right heart. Pulmonary hypertension, thromboembolism pulmonary artery, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and other diseases can cause the development of right atrial insufficiency.

Left ventricle. For the ventricles, their own parameters have been introduced regarding their size. Since the functional state of the ventricles in systole and diastole is of interest to the practitioner, there are corresponding indicators. Main dimensions for LV:

Right ventricle. Basal diameter — ≤ 41 mm;
End diastolic volume (EDV) RV/BCA (men) ≤ 87 ml/m2, women ≤ 74 ml/m2;
End systolic volume (ESV) of the RV / BCA (men) - ≤ 44 ml / m2, women - 36 ml / m2;
The wall thickness of the pancreas is ≤ 5 mm.
Interventricular septum. The thickness of the IVS in men in mm is ≤ 10, in women it is ≤ 9;
4 Valves

Echocardiography uses parameters such as valve area and mean pressure gradient to evaluate the condition of the valves.
- aortic valve. Area - 2.5-4.5 cm2; mean pressure gradient
- Mitral valve (MK). Area - 4-6 cm2, average pressure gradient
5 Vessels

Pulmonary artery. Pulmonary artery (PA) diameter — ≤ 21 mm, LA acceleration time — ≥110 ms. A decrease in the lumen of the vessel indicates stenosis or pathological narrowing. Systolic pressure ≤ 30 mm Hg, mean pressure ≤ 20-25 mm Hg; An increase in pressure in the pulmonary artery, exceeding the permissible limits, indicates the presence of pulmonary hypertension.
Inferior vena cava. Inferior vena cava (IVC) diameter — ≤ 21 mm; An increase in the inferior vena cava in diameter can be observed with a significant increase in the volume of the right atrium (RA) and a weakening of its contractile function. This condition can occur with narrowing of the right atrioventricular orifice and with insufficiency of the tricuspid valve (TC).
Other sources provide more detailed information on other valves, large vessels, and performance calculations. Here are some of them that were missing above:
- The ejection fraction according to Simpson is the norm ≥ 45%, according to Teicholz - ≥ 55%. Simpson's method is used more often, as it has greater accuracy. According to this method, the entire LV cavity is conditionally divided into a certain number of thin discs. The EchoCG operator at the end of systole and diastole makes measurements. The Teicholz method for determining the ejection fraction is simpler, however, in the presence of asynergic zones in the LV, the obtained data on the ejection fraction are inaccurate.
- The concept of normokinesis, hyperkinesis and hypokinesis. Such indicators are estimated by the amplitude of the interventricular septum and the posterior wall of the left ventricle. Normally, the fluctuations of the interventricular septum (IVS) are in the range of 0.5-0.8 cm, for the posterior wall of the left ventricle - 0.9 - 1.4 cm. If the amplitude of movements is less than the indicated figures, they speak of hypokinesis. In the absence of movement - akinesis. There is a concept and dyskinesia - the movement of the walls with a negative sign. With hyperkinesis, the indicators exceed normal values. Asynchronous movement of the LV walls may also occur, which often occurs in violation of intraventricular conduction, atrial fibrillation (AF), artificial pacemaker.
site - medical portal about the heart and blood vessels. Here you will find information about the causes, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, traditional and folk methods treatment of cardiac diseases in adults and children. And also about how to keep the heart healthy, and the blood vessels clean until the most advanced years.
Do not use the information posted on the site without first consulting with your doctor!
The authors of the site are practicing medical specialists. Each article is a concentrate of them personal experience and knowledge honed by years of study at the university, received from colleagues and in the process of postgraduate training. They not only share unique information in articles, but also conduct a virtual reception - they answer questions that you ask in the comments, give recommendations, and help you understand the results of examinations and appointments.
All topics, even those that are very difficult to understand, are presented in a simple, understandable language and are designed for readers without medical training. For your convenience, all topics are divided into categories.
Arrhythmia
According to the World Health Organization, more than 40% of people over 50 years of age suffer from arrhythmias - heart rhythm disturbances. However, not only they. This insidious disease is detected even in children and often in the first or second year of life. Why is he cunning? And the fact that sometimes disguises pathologies of other vital organs as heart disease. Another unpleasant feature of arrhythmia is the secrecy of the course: until the disease goes too far, you can not guess about it ...
- how to detect arrhythmia at an early stage;
- what forms of it are most dangerous and why;
- when the patient is enough, and in what cases it is impossible to do without surgery;
- how and how long they live with arrhythmia;
- which attacks of rhythm disturbance require an immediate call to an ambulance, and for which it is enough to take a sedative pill.
And also all about the symptoms, prevention, diagnosis and treatment various kinds arrhythmias.
Atherosclerosis
The fact that the main role in the development of atherosclerosis is played by an excess of cholesterol in food is written in all the newspapers, but why then in families where everyone eats the same way, only one person often gets sick? Atherosclerosis has been known for more than a century, but much of its nature has remained unsolved. Is this a reason to despair? Of course not! The specialists of the site tell what success modern medicine has achieved in the fight against this disease, how to prevent it and how to effectively treat it.
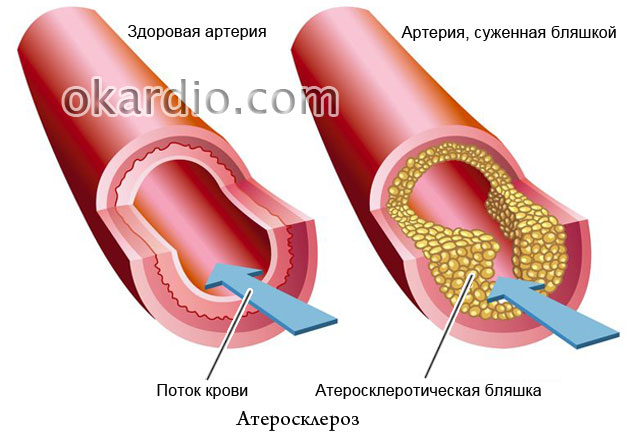
- why margarine is more harmful than butter for people with vascular disease;
- and how dangerous it is;
- why cholesterol-free diets do not help;
- what will have to be abandoned for life by patients with;
- how to avoid and maintain clarity of mind until old age.
Heart diseases
In addition to angina pectoris, hypertension, myocardial infarction and congenital heart defects, there are many other cardiac ailments that many have never heard of. Do you know, for example, that - not only the planet, but also the diagnosis? Or that a tumor can grow in the heart muscle? The heading of the same name tells about these and other diseases of the heart of adults and children.
- and how to provide emergency care the patient in this condition;
- what and what to do so that the first does not pass into the second;
- why the heart of alcoholics increases in size;
- what is the danger of mitral valve prolapse;
- what symptoms can be suspected of heart disease in yourself and your child;
- which cardiac ailments threaten women more, and which ones men.

Vascular diseases
Vessels permeate the entire human body, so the symptoms of their defeat are very, very diverse. Many vascular ailments at first disturb the patient a little, but lead to terrible complications, disability and even death. Can a person without medical education identify vascular pathology in himself? Of course, yes, if he knows their clinical manifestations, which this section will tell about.
In addition, it contains information:
- about medicines and folk remedies for the treatment of blood vessels;
- about which doctor to contact if you suspect vascular problems;
- what vascular pathologies are deadly;
- what causes veins to swell;
- how to maintain the health of veins and arteries for life.
Varicose veins
Varicose veins (varicose veins) is a disease in which the lumens of some veins (legs, esophagus, rectum, etc.) become too wide, which leads to impaired blood flow in the affected organ or part of the body. In advanced cases, this ailment is cured with great difficulty, but in the first stage it is quite possible to curb it. How to do this, read in the section "Varicosis".
 Click on photo to enlarge
Click on photo to enlarge You will also learn from it:
- what ointments exist for the treatment of varicose veins and which one is more effective;
- why doctors forbid some patients with varicose veins of the lower extremities to run;
- and to whom it threatens;
- how to strengthen veins with folk remedies;
- how to avoid the formation of blood clots in the affected veins.
Pressure
- such a common ailment that many consider it ... a normal condition. Hence the statistics: only 9% of people suffering from high pressure keep it under control. And 20% of hypertensive patients consider themselves healthy at all, since their disease is asymptomatic. But the risk of getting a heart attack or stroke from this is no less! although less dangerous than high, it also causes a lot of problems and threatens with serious complications.

In addition, you will learn:
- how to “deceive” heredity if both parents suffered from hypertension;
- how to help yourself and loved ones with a hypertensive crisis;
- why blood pressure rises at a young age;
- how to keep blood pressure under control without medication healing herbs and certain products.
Diagnostics
The section devoted to the diagnosis of diseases of the heart and blood vessels contains articles on the types of examinations that cardiac patients undergo. And also about the indications and contraindications to them, the interpretation of the results, the effectiveness and procedure for the procedures.
You will also find answers to questions here:
- what types of diagnostic tests even healthy people should undergo;
- why angiography is prescribed for those who have had myocardial infarction and stroke;

Stroke
Stroke ( acute disorder cerebral circulation) is consistently among the ten most dangerous diseases. People over 55 years of age, hypertensive patients, smokers and those who suffer from depression are at the greatest risk of its development. It turns out that optimism and good nature reduce the risk of strokes by almost 2 times! But there are other factors that effectively help to avoid it.
The section on stroke tells about the causes, types, symptoms and treatment of this insidious disease. And also about rehabilitation measures that help restore lost functions to those who have had it.

In addition, here you will learn:
- about the difference clinical manifestations strokes in men and women;
- about what a pre-stroke state is;
- about folk remedies for the treatment of the consequences of strokes;
- about modern methods quick recovery after suffering a stroke.
heart attack
Myocardial infarction is considered to be a disease of older men. But it still poses the greatest danger not to them, but to people of working age and women over 75 years old. These groups have the highest mortality rates. However, no one should relax: today, heart attacks overtake even young, athletic and healthy people. More precisely, unexplored.
In the "Heart attack" section, experts talk about everything that is important to know for everyone who wants to avoid this disease. And those who have already suffered a myocardial infarction will find here a lot useful tips for treatment and rehabilitation.

- about what diseases are sometimes disguised as a heart attack;
- how to provide emergency care acute pain in the region of the heart;
- about the differences in the clinic and the course of myocardial infarction in men and women;
- about an anti-infarction diet and a safe lifestyle for the heart;
- about why a heart attack patient must be taken to the doctor within 90 minutes.
Pulse disorders
Speaking of pulse disorders, we usually mean its frequency. However, the doctor evaluates not only the patient's heart rate, but also other indicators of the pulse wave: rhythm, filling, tension, shape ... The Roman surgeon Galen once described as many as 27 of his characteristics!

The change in individual parameters of the pulse reflects the state of not only the heart and blood vessels, but also other body systems, for example, the endocrine system. Do you want to know more about it? Read the rubric.
Here you will find answers to questions:
- why, if you complain of pulse disorders, you may be referred for a thyroid examination;
- whether a slow heart rate (bradycardia) can cause cardiac arrest;
- what does it say and why is it dangerous;
- how heart rate and fat burning rate are related when losing weight.
Operations
Many diseases of the heart and blood vessels, which 20–30 years ago doomed people to lifelong disability, are successfully cured today. Usually surgical. Modern cardiac surgery saves even those who until recently did not leave any chance for life. And most operations are now carried out through tiny punctures, and not incisions, as before. This not only gives a high cosmetic effect, but is also much easier to tolerate. And also reduces the time of postoperative rehabilitation several times.
In the section "Operations" you will find materials about surgical methods treatment varicose veins veins, vascular bypass, installation of intravascular stents, prosthetic heart valves and much more.
You will also learn:
- what technique does not leave scars;
- how operations on the heart and blood vessels affect the quality of life of the patient;
- what are the differences between operations and vessels;
- at what diseases it is carried out and what is the duration of a healthy life after it;
- what is better for heart disease - to be treated with pills and injections or to have an operation.

Rest
The "Other" includes materials that do not correspond to the topics of other sections of the site. It contains information about rare cardiac diseases, myths, misconceptions and interesting facts concerning heart health, about incomprehensible symptoms, their meaning, about the achievements of modern cardiology and much more.
- about providing first aid to yourself and others in various emergency conditions;
- about the child;
- about acute bleedings and methods of their stop;
- about and eating habits;
- about folk methods of strengthening and improving the cardiovascular system.

Preparations
“Drugs” is perhaps the most important section of the site. After all, the most valuable information about the disease is how to treat it. We do not present here magic recipes for curing serious ailments with one tablet, we honestly and truthfully tell everything about the drugs as they are. What are they good and bad for, who are indicated and contraindicated, how they differ from analogues and how they affect the body. These are not calls for self-treatment, this is necessary so that you are well versed in the “weapon” with which you will have to fight the disease.

Here you will find:
- reviews and comparison of drug groups;
- information about what can be taken without a doctor's prescription, and what should not be taken in any case;
- a list of reasons for choosing one or another means;
- information about cheap analogues of expensive imported drugs;
- data on side effects heart drugs that manufacturers are silent about.
And many, many more important, useful and valuable things that will make you healthier, stronger and happier!
May your heart and blood vessels always be healthy!
